What is semantic segmentation?
Semantic segmentation involves understanding not just what happens to be in the scene, but also what regions of the image those things are located in, at a very fine-grained level. it is easiest to understand it by comparing it to image classification and object detection.
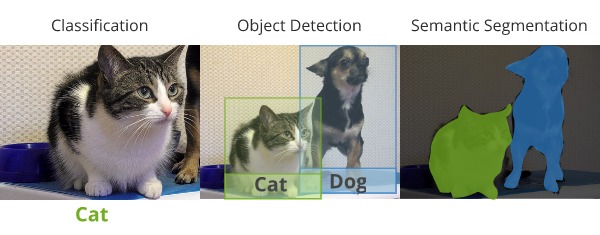
In image classification, we simply care about making a prediction about what class of object is in the scene. Object detection is about making predictions over potentially multiple objects in the scene, and getting a rough idea of where they are located. The localization of the objects just needs to be good enough to draw bounding boxes around the objects.
For segmentation, we care about locating the regions taken up by the different objects with much more detail. We would like to create precise outlines of the objects in the scene. The idea is actually to identify exactly which pixels belong to different objects.
Where is it used?
Semantic segmentation is quite useful in several different industries. It is an important component for self-driving cars, which need to be able to identify regions of the environment that occupied by other cars, identifying where the road is, where obstacles are located and also identifying where any pedestrians are located.
It is useful in medical applications. For instance for identifying and highlighting the regions occupied by different types of cells. Or even identifying cancerous cells.
It can also be used for augmented reality applications, where you may want to overlay things over precise regions that contain items of interest.